
Although this can be a time-taking procedure, this will help confirm the diagnosis. To confirm the presence of the fungi, a scalp or hair sample might be taken.

Sometimes, to get a wider picture, your doctor may use a Wood’s lamp to illuminate your scalp to check for signs of infection. Dotted appearance like that of a stubble due to broken hair shaftsĪ visual examination of the scalp is enough for the doctor to get an idea of your condition.Round patches marked by hair loss moving towards an increased size.Frizzy hair with a tendency to break when pulled out.Ringworm of the scalp presents itself on the scalp as: Tinea capitis starts damaging your hair and the outer layer of your scalp as soon as the fungal colony inhabits the scalp. Symptoms Associated with Ringworm of the Scalp Indirect contact: This is also known as fomite transmission, wherein the fungal spores are transmitted through a channel of contaminated objects such as bedding, pillow, towel, hairbrush, and head coverings such as a scarf, hat, and cap.Direct contact: This is the direct transmission of fungal spores from an infected person or an infected animal such as a cat, dog, goat, horse, cow, and a pig.The infection can be transmitted either through: The former is transmitted through human contact, and the latter is transmitted from an animal, such as a dog and a cat, to a human. The majority of the fungi that inhabit and infect the human scalp are Trichophyton and Microsporum classified according to the route of transmission. Ringworm is caused by a dermatophyte fungus. Complications Related to Ringworm of the Scalp.Standard Treatments for Ringworm of the Scalp.How is Ringworm of the Scalp Diagnosed?.Symptoms Associated with Ringworm of the Scalp.Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of a Tinea Capitis Outbreak among Novice Buddhist Monks. The authors proposed that educational efforts regarding avoiding sharing personal items and improvement in personal and environmental hygiene is needed to reduce infection.īunyaratavej et al.
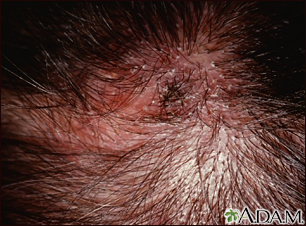
Much to my surprise, 95 % of the monks had evidence of scarring alopecia - a feared complication of tinea capitis type infections.

Microsporum canus (common in Europe) was less commonly found (35 %) and Trichophyton tonsurans (common in North America) was found in only 13 % of cases. Many different types of fungi were uncovered from scalps included the anthropophilic fungus Trichophyton violaceum (60 %) and Trichophyton mentagrophytes (43 %). In this study, 60 young male Buddhist monks with tinea capitis were studied. People living in close contact and sharing combs and similar type material are at higher risk for acquiring tinea capitis.Ī recent study from Thailand has some important lessons about tinea capitis. Tinea capitis is common among children and rare in adults. As we've seen this week, "tinea capitis" refers to infection of the scalp by various types of fungi.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
